Iv fluid therapy (types, indications, doses calculation)
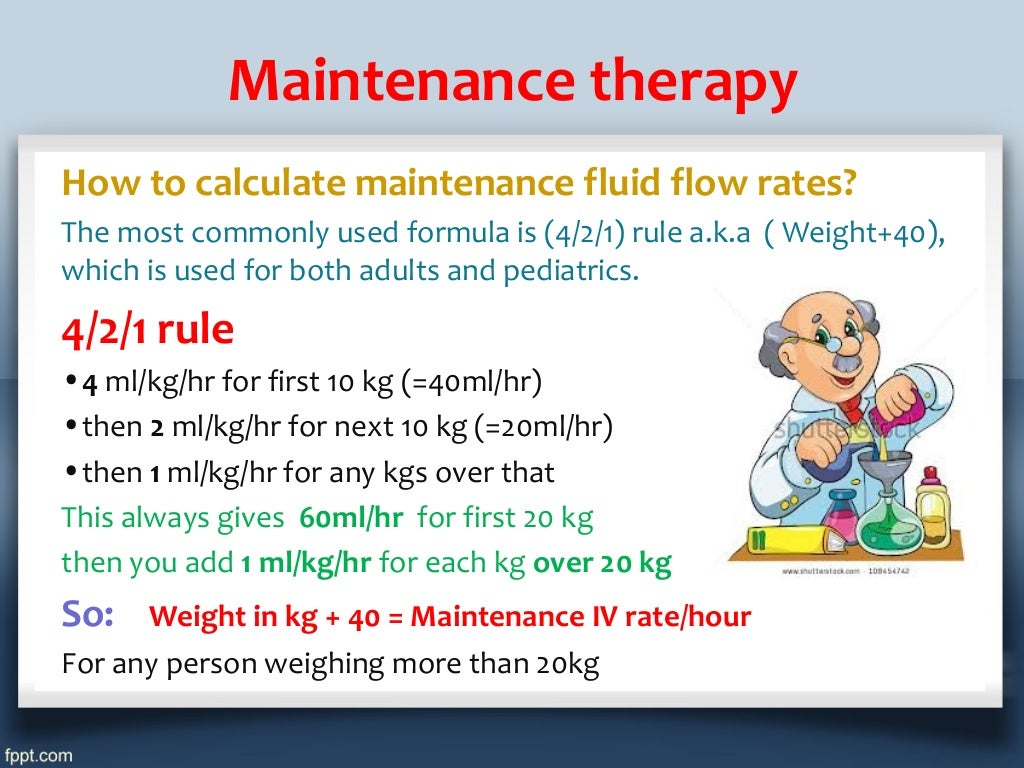
Calculating IV Fluid Rate/Volume. Caution should be exercised in using "maintenance" IV fluids at rates above the calculated maintenance; fluid replacement should be calculated separately to account for ongoing losses. 4-2-1 rule (100-50-20 rule) 4 mL/kg/hr (100 mL/kg/day) for the first 10kg PLUS. 2 mL/kg/hr (50 mL/kg/day) for the second 10kg PLUS.

Buy IV Fluid Solution Bags for IV Therapy online used to treat Intravenous Solution Medical
Normal saline solution can be administered only via intravenous (IV) access. 0.9% Normal Saline (NS, 0.9NaCl, or NSS) is one of the most common IV fluids, it is administered for most hydration needs: hemorrhage, vomiting, diarrhea, hemorrhage, drainage from GI suction, metabolic acidosis, or shock. It is an isotonic crystalloid that contains 0..

IV Fluid Solution_Shanghai Marya Pharmaceutical Engineering & Project Co., Ltd
IV fluids are specially formulated liquids that are injected into a vein to prevent or treat dehydration. They're used in people of all ages who are sick, injured, dehydrated from exercise or heat, or undergoing surgery. Intravenous rehydration is a simple, safe and common procedure with a low risk of complications.

IV FLUIDS TYPES; Functions and Indications for Use NurseHuman
Solution 2/3-1/3 D5W & Normal Saline 1L. Solution 2/3 +1/3 40 mEq of KCL per 1L Solution 2/3-1/3 D5W & Normal Saline 500mL. Solution 2/3-1/3 D5W & Normal Saline 1L Code: IVSOL0011. Vendor: Code: Calea JB1034X. Manufacturer: Code: Baxter. JB1034. Ask a question about this product. Product Categories. Enteral Supplies. Adaptors.

IV Fluids (Intravenous Fluids) The 4 Most Common Types
IV fluids are a cornerstone of healthcare, essential for maintaining fluid balance, regulating electrolyte levels, and delivering life-saving interventions. Whether in the clinical setting or as a therapeutic tool, their precise administration is vital to patient care. In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the types of IV fluids.

1/2 normal saline for hypernatremia
The following table gives the composition of IV fluids that are commercially available and commonly used for neonates, infants and children. For a decision on which fluid to use in particular circumstances, see the disease-specific chapters, e.g. for shock (Chart 8), for neonates (section 3.10.2), for severely malnourished children (section 7.4.3), for surgical procedures (section 9.1.3) and.

The Vitals IV Fluids Compositions and Choices CriticalCareNow
1.1.1 Assess and manage patients' fluid and electrolyte needs as part of every ward review. Provide intravenous (IV) fluid therapy only for patients whose needs cannot be met by oral or enteral routes, and stop as soon as possible. 1.1.2 Skilled and competent healthcare professionals should prescribe and administer IV fluids, and assess and.

Intravenous Fluids Types of IV fluids Health And Willness Nursing school survival, Nursing
1.3.1. If patients need IV fluid resuscitation, use crystalloids that contain sodium in the range 130-154 mmol/l, with a bolus of 500 ml over less than 15 minutes. (For more information, see the Composition of commonly used crystalloids table.) 1.3.2. Do not use tetrastarch for fluid resuscitation. 1.3.3.

Physician Assistant, Finally There What's in IV Fluid Anyway? Nurse, Icu nursing, Nursing tips
The rate of fluid dripping from a bag into an IV can be regulated through a manual technique. Your nurse increases or decreases the pressure that a clamp puts on an intravenous tube to either slow.
Iv Fluids Types Rnnursingexam
If patient not euvolemic after 40 mL/kg of isotonic fluid: 1. Consider other sources of fluid loss 2. Consider escalating care 3. Patient no long meets IV Fluid Pathway criteria - off pathway! Prior to starting a patient on maintenance IV fluids, consider the following: • Risk factors for abnormal ADH secretion • Initial electrolyte.

Dextrose Iv Fluids
There are different ways that IV fluids or medications can be given, and most of the subtypes of IV administration are listed below.. and normal saline. The common abbreviation is 2/3-1/3. 5% dextrose in water: This solution is a mixture of dextrose (sugar) and water. The percentage indicated can vary depending on the level of dextrose in.
&srotate=0)
What Makes You a Candidate for IV Nutrition?
38.93. [ edit on Wikidata] Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or.

Intravenous Fluids
• Patients should have an IV fluid management plan, which should include details of: - The fluid and electrolyte prescription over the next 24 hours - The assessment and monitoring plan. Initially, the IV fluid management plan should be reviewed by an expert daily. IV fluid management plans for patients receiving longer term IV fluid
IV Fluids Lesson 1 Basic Principles YouTube
2. Hypotonic IV Fluids . Hypotonic fluids have low levels of solutes and help to draw water into cells. Here are some examples of commonly-used hypotonic IV fluids: 0.225% Sodium Chloride (NaCl 0.225%) 0.225% sodium chloride solution, which may also be referred to as or 0.225% NaCl, is a type of sodium chloride solution.
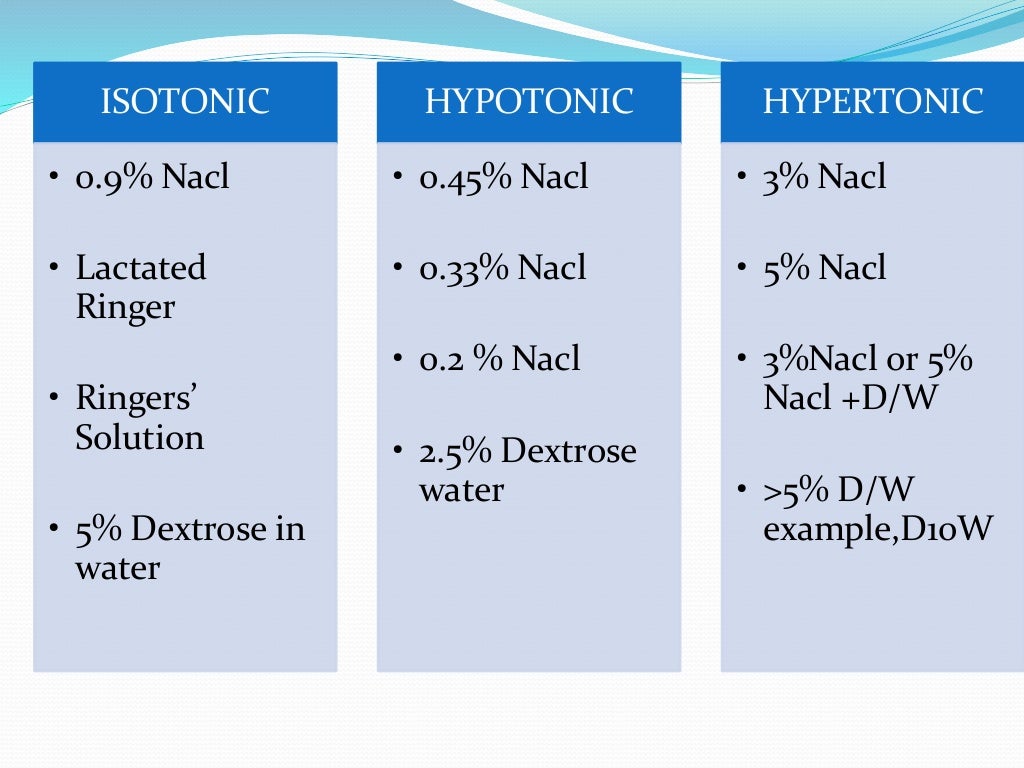
Iv fluids
0.9% NaCl (Normal Saline Solution, NSS) Normal saline solution (0.9% NaCl) or NSS, is a crystalloid isotonic IV fluid that contains water, sodium (154 mEq/L), and chloride (154 mEq/L). It has an osmolality of 308 mOsm/L and gives no calories. It is called normal saline solution because the percentage of sodium chloride dissolved in the solution is similar to the usual concentration of sodium.

Types Of Iv Fluids Intravenous Fluid Comparison Type Solution Uses
1 Introduction2 Crystalloids2.1 Dextrose2.2 Normal Saline2.3 Hartmann's Solution2.3.1 Hartmann's Solution and Acidosis3 Colloids4 Key Points Introduction Fluid management is an essential part of a junior doctor's practice and hence knowledge of the composition for each intravenous fluid prescribed is essential. This article discusses the composition of commonly prescribed crystalloids.
- Toyota Tacoma Truck Bed Mat
- Hydra Evolution Electric Boiler Troubleshooting
- Macaron Noix De Coco Santé
- Santa Claus Beard And Wig
- Purple Martin Houses For Sale
- Townhouse For Rent Fort Mcmurray
- Land For Sale By The Owner
- Gateau Dans Une Tasse A La Vanille
- Down For It All Hoodie
- House For Sale In Harbour Landing Regina